Sales is hard. Selling software as a service (SaaS) is much more complex. Buyers are spoiled for choices. They prefer self-service, and they do their own research.
But the purchasing process often involves many stakeholders and multiple touchpoints. Decision makers change frequently.
The contract sizes are smaller. In this situation, closing a sales deal is not an easy task. Fortunately, there’s more than one strategy to sell SaaS.
Whether you are new to SaaS sales or want to refresh, and add new strategies to your sales handbook, this article has something valuable for you.
This post covers the following:
- What is SaaS?
- What are SaaS sales?
- Why is selling SaaS different?
- What are the types of sales strategies?
- What are the top six strategies to sell SaaS?
What is SaaS?
Software marketplace G2 defines SaaS as “a software licensing and delivery model in which the software is hosted by a vendor or service provider, enabling access from multiple users or devices.”
Think about your Netflix subscription. Just like you pay Netflix to stream movies and shows, you pay a software vendor to use their product over the internet. Payment is perused, and the vendors maintain the required software and hardware. It saves the customer money, and circumvents the annoyance of managing the underlying infrastructure for software.
Name any business function: emails, messaging, video conferencing, web design, file sharing, customer relationship management (CRM), marketing, IT, and human resource management. Whatever the case, there’s a SaaS for that. There are even SaaS application that monitor a company’s software stack.
SaaS is accessible, affordable, and easy to use – precisely why its adoption is reaching dizzying heights today. Companies with fewer than 750 employees use about 60 different SaaS apps, mid-sized organizations use about 140, and large enterprises use more than 450.
The global SaaS market is estimated surge to $10 trillion by 2030 from $3 trillion today. So there’s no better time than now to be in the SaaS business. But growing a SaaS company is challenging in this competitive, and fast-changing environment.
SaaS products solve nagging problems for many businesses, and make people’s lives easier. So they should sell themselves. But they don’t, no matter how good the product might be. You must show your prospects what you have, and how it solves their problems.
Moreover, there are probably more companies offering the same SaaS product as you are. So, SaaS vendors need to be on top of the game to win customers. And that’s where SaaS funding & sales come in.
What is SaaS sales?
SaaS sales is the process of selling web-based software to buyers on a pay-per-use model. SaaS buyers can be individuals, small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs), enterprises, or agencies.
Since SaaS is commonly sold on a subscription basis, sales is all about finding new prospects, upselling, and retaining existing clients when it’s time for renewal. This means the company should have a clear sales process, and long-term strategy to keep the subscriptions rolling in.
SaaS sales process
A typical SaaS sales process in a B2B company or a startup involves the following seven steps: prospecting, preparation, approach, presentations, handling objections, closing, and follow-up. How long it takes from prospecting to closing the deal differs from company to company.
SaaS sales cycles depend on product complexity, pricing, and target customers. A simple SaaS product development with a low price of $30 per month that targets small and medium businesses has a short sales cycle.
Why is selling SaaS different?
Selling SaaS is different majorly because of three reasons:
Finding qualified leads for SaaS products is difficult
Imagine selling a car. A customer comes to the car showroom, and the salesperson asks questions to understand their need and zero in on the ideal model for the customer.
Generating quality leads is an essential part of business success, and utilizing tools such as LinkedIn Email finder can help to make this process easier and more efficient.
On the other hand, only a few customers come directly to an email automation software company asking for the product. Instead, the sales and marketing team has to work hard to find leads. Once they do, they need to take a highly targeted approach to create a personalized customer journey, addressing all their pain points.
SaaS Products are complex
So now you have a lead for your email automation software. You need to explain to the prospect how the software works. Your prospect has many questions about its working, email deliverability, and bounce rates, among many other issues. Sales reps need to know all the technicalities of the software to answer the questions.
Sometimes, this requires involvement from the sales team and marketing or product engineering team to make a successful sale.
Selling SaaS is a perpetual cycle
A G2 survey of business-to-business (B2B) buyers found that 57% of software contracts are for six months or fewer. It shows SaaS sales can’t be a one-off transaction. For example, if your lead bought the email automation software subscription, the sales process continues. They need to be convinced to continue with their subscription, and renew it. Otherwise, the organization has a low retention rate and a high customer churn rate.
Why SaaS sales strategies are important?
Today is the age of buyers. A glut of high-quality software options and easy access to product and market information have turned customers into royalty. They’re looking for the least friction possible when adding a SaaS solution to their tech stack.
But a quarter of companies don’t even have a software buying process, according to the G2 survey. Maybe not be surprising since more than 20 distinct roles get involved in the software buying process.
Adding to the challenges is that buyers don’t go for multiyear software contracts. Only 11% of B2B software buyers sign software contracts for over two years. Half of the customers consider alternatives when a product is up for renewal, and the cost-to-switch for buyers in a cloud-based world is lower than ever.
Such a demanding market puts extreme pressure on SaaS sales teams. They need several sales strategies to win.
Two major types of SaaS sales strategies
Before we delve deeper into different sales strategies, let’s look at two main types of sales strategies.
Inbound sales strategy
The inbound sales strategy attracts customers who know what they want or what problem they want to solve. Remember the car showroom example where a customer walked in to buy a car? Such prospects are inbound leads.
The buyer initiates the conversation. The company figures out a customer’s pain points, and goals to position its products as the best solution. Inbound sales strategies are best suited to create awareness about your product, and get a hold of warm leads.
Outbound sales strategy
Outbound sales strategy is more like casting a wide net to find people who might be potential customers. The seller initiates the conversation, and charms potential customers, via cold emails, messages, demos, and free trials. Outbound sales strategies are best suited when the company has a clear value proposition and targeted buyer persona.
For example, healthcare brands use digital HCP engagement platforms to share and generate relevant sales for their healthcare business.
Naturally, a question arises now: which sales strategy is best suited for SaaS companies, inbound or outbound?
Inbound vs. outbound sales strategies
In truth, both are. While inbound targets warm up leads, outbound looks to create leads. So both become essential in having a growing sales pipeline. Any SaaS business should find the right mix of inbound and outbound sales strategies based on sales factors like ideal customer profile, buyer behavior, and current market trends.
Top six SaaS sales strategies with examples
Different factors like buyer persona, behavior, actions, position in the sales pipeline, and current market trends influence the kind of sales strategy a company needs to adopt. When you plan your SaaS sales strategy, consider the following:
- What product do we sell?
- Who do we sell to?
- How and where do we sell?
- What problems do we solve?
Answering these questions lead you to your business goals, target market, and ideal customer profiles. Once you know this, selecting your SaaS sales model, and crafting your sales strategy is relatively easy. Check out these proven SaaS sales strategies to boost your sales.
1. Execute an SEO strategy
Successful SaaS companies have a clear search engine optimization (SEO) strategy. Why? The #1 result in Google’s organic search results has an average click-through rate of 27.6%, and the top 3 search results get 54.4% of all clicks. SEO helps your website land on the first page of organic search and find new leads without spending a dime on ads.
Take someone who is searching for email automation. Out of the 1,470,000,000 results on the search engine results page (SERP), people will click on sites like Mailchimp and Campaign Monitor from the first page.
This is where your SEO efforts come in. Follow these steps to get your website’s SEO in order.
- Audit your SaaS website. Fix technical website issues to ensure your site is easy to find on Google.
- Find keywords. Imagine you’re selling email marketing software. Keywords in the category aren’t just email marketing or email marketing tools. They also include digital marketing, how to create email lists, how to send email campaigns, templates for email campaigns, drip campaigns, what is a/b testing, open rate, email deliverability – you get the idea. In short, find related keywords for your SaaS products and also other information your customers might use to search.
Hubspot ranks for more than 4 million keywords. It’s not just their product keywords but also things like digital marketing, small business ideas, blogging, or lead generation. So figure out what your customers are searching for, and provide answers to those queries.
- Create content. Once you have a list of keywords, create high-quality content on keywords and publish consistently. You should also create lead magnets with gated content like eBooks, whitepapers, and case studies.
- Get high-quality links. Implement an off-page SEO strategy where you boost your domain authority with internal links and backlinks from other authority websites. Don’t pay for backlinks. While it looks good in the short term, Google penalizes you for it with sudden drops in traffic and rank. Make sure to have a great link building strategy as it is important to add high value links to your backlink portfolio.
- Track and optimize. Track your website performance, compare it with your competitors, and change your SEO methods to get the maximum results.
Remember, each SaaS business can have a different SEO strategy to get maximum organic traffic. Once you gain traction, use lead mining software to find your website visitors.
2. Price intelligently
Pricing directly impacts your SaaS product positioning, packaging, and revenue. A poorly-framed system drives away potential customers, leaving revenue on the table. So come up with a concrete pricing strategy. Your pricing needs to convert more leads, and close more SaaS deals. Try out these tips to get your product pricing right.
- Base your pricing on your product value and the price your users are willing to pay.
- Segment your buyer personas. This is critical for building different pricing tiers for different target audiences. A small business’s budget for your product may not be the same as an enterprise customer’s.
- Package your product in diverse plans for diverse target groups. Pricing models a SaaS company can use are:
- Usage-based pricing
- Tiered pricing for customer groups at various price points
- Per user pricing
- Per feature pricing
- Per active user-based pricing
Select a model depending on your product value, features, and buyer personas.
- Survey your leads about what they are willing to pay. Ask them what price point they consider cheap, expensive, too cheap, or too expensive for your product packages. The middle range of prices among the four hits the optimal pricing.
- Once you set your pricing, track how well your customers receive it.
Experiment with various pricing strategies to see what works for you. Try pricing your product below your competitors. Or start offering your product at the lowest possible price, and slowly increase once you attract a large user base. You can even charge low for your core offerings and extra for additional features. There’s no one-size-fits-all here. Keep experimenting with your pricing until you find your sweet spot.
3. Be strategic with free trials
Free trials are a way to say to a potential customer, “Take my product for a test drive. Pay if you think it’s worth the money.”
It’s a great method to acquire new leads quickly. Be clever about how you plan your free trials. Your strategy should be able to convert a maximum number of paying subscribers. Generally, businesses use three different types of free trials.
An opt-in free trial offers a free trial of a product for a limited time without payment information from the user. This option lowers the entry barrier to a bare minimum of signing up. However, it requires creating a great product service during their trial that compels leads to buy or subscribe to the product.
An opt-out free trial requires upfront payment information to provide full use of the product for a limited time. After the trial period ends, the user automatically becomes a subscriber of the product. If they want to unsubscribe, they have to opt-out actively.
Freemium indefinitely gives users a free version of the essential product or features, and charges for additional features. The freemium option is used to acquire new customers or disrupt an incumbent competitor rapidly. Canva, Dropbox, Zoom, and Slack are famous examples of SaaS companies succeeding with the freemium option.
Before deciding on your free trial model and period, consider the following:
- How mature is the product or brand?
If your product is new and you want to grow your user base, a freemium or opt-in trial would suit the business. On the other hand, if your brand is well-established, it’s easier to go for an opt-out free trial.
- How much time does the user need to fully understand the product or service value?
The common trial period lengths are
- 7 days for a simple product with straightforward features.
- 14 days for a slightly complex product.
- 30 days for a complex product that requires time to fully understand its features.
Whether it’s a shorter or longer trial period, the user needs to have an “aha” moment with the product that convinces them to buy the subscription. If you have many free trial users and a low conversion rate, then the free trial isn’t useful. To avoid this, consider the following tips:
- Have a frictionless free-trial signup.
- Communicate the trial expectations clearly.
- Keep in touch with trial users, from welcome emails to feedback emails.
- Automate prompts and messages based on user activity.
- Nurture your trial users. Share tips, tricks, and examples of how to use your product to its best potential.
- Be ready to provide support at any time. Use chatbots or online assistance.
- Make it easy to upgrade from free trials.
- Make it very easy to opt-out of free trials.
- Always remind the users to upgrade their plan.
- Keep optimizing your free trials. There’s always room for more conversions.
Chargebee optimized its free trial, added user experience nudges, and changed the demo it offers according to different buyer personas. The adjustments increased its free trial-to-paid conversion rate increase from 8% to 15%.
4. Jump on other channel sales
Use third parties like affiliate marketers to sell your products or services. A third-party intermediary helps you indirectly sell the product, and get a commission on the sale. This strategy helps your company distribute the product outside of your sales and marketing channels without increasing your sales team headcount. A variety of channel sales models are there to choose from.
- Affiliate partners (bloggers, industry influencers)
- Value-added resellers
- Managed service providers
- Marketplace
- Distributors
- Consultants
- System integrators
Before tapping into channel sales, make sure you assess whether your product or service is ready. If you’ve just released your product and haven’t found your first few customers, refrain from using channel sales. On the other hand, if your product already has an established user base, and you’re looking to expand it to new users, try channel sales.
Decide on the type of channel partners. Your ideal partner profile depends on these factors:
- Product/service complexity
- Your target market
- Your buyer personas
- Your sales process
- Revenue goals
Once you decide on the channel partner type, get a list of potential partners, and assess them. Make sure the partners you select have a good understanding of the audience you want to reach. They should be experts in the product category you operate in, and have the resources to market and sell your product. Once you zero in on your partners, set up your internal structure to support them when needed.
Many SaaS companies like ActiveCampaign, Shopify, and Hubspot have affiliate partner programs that generate millions of dollars in revenue.
5. Upsell and cross-sell
Upselling and cross-selling to existing customers are one of the cost-effective ways to boost your revenue. No customer acquisition cost is involved in this strategy. The success rate of selling to an existing customer is 60% – 70%. Selling to a new prospect, on the other hand, only has a 5% – 20% success rate. Read on to learn a few ways to upsell and cross-sell.
- Get add-ons to your product plans. These should be features customers should be willing to shell out extra money for. See this example from Dialpad’s business communication software. Apart from the standard product plans, they display add-ons that customers can purchase.
- When your user hits the resource limit of their current product plan, prompt them to upgrade. Google always reminds Gmail account users to buy a storage plan when they approach their free storage quota of 15GB.
- Inform and nudge users to upgrade when you add a new feature or a product. You can even offer a free trial of new features to customers, and convert them later.
- Bundle related products into packages, and offer flexible pricing when you cross-sell. Adobe has a great bundle of Creative Cloud and Document Cloud.
- Track your buyer behavior to find new upselling and cross-selling opportunities. Promote what other customers have already purchased. An example of this is the “Frequently bought together” section on Amazon.
Make sure to train your salespeople with specific upselling and cross-selling pitches for your SaaS product.
6. Create a referral program
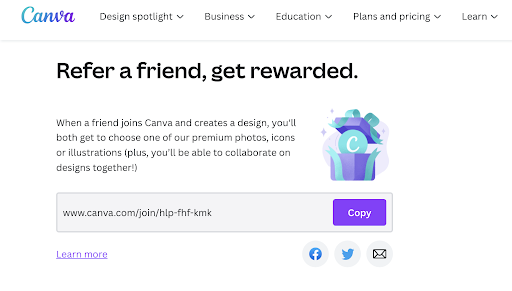
If you think referral won’t work for SaaS products, think again. SaaS companies like Canva, Dropbox, Airtable, Trello, and Evernote have great referral programs that drive quality leads. In fact, research shows eight out of ten people trust recommendations from known contacts, and are four times more likely to make a purchase based on a good suggestion.
Plus, referrals are a win-win. Customers refer, and find more leads for you while you give them an attractive incentive. For example, look at the referral program by Dropbox that offers extra storage as a bonus. Getting up to 16 GB and 32GB of storage space encourages users to find more referrals to get that free space.
Design your referral program to get customers to keep referring. Give your customers a reason to share your product.
Provide exceptional customer experience and make your current customers your best brand advocates. Research to find out what kind of incentive your customers might like.
Canva gives one of its premium photos, icons, or illustrations for design as an incentive. On the other hand, Zoho provides 15% of the subscription fee as a referral incentive if one of the referrals buys a subscription.
Make your referral program easy to use with simple links. Most importantly, track your referrals, and reach out to them quickly to nurture those leads. You can also use dynamic QR code generators to create custom QR codes for your referrals, these reusable QR codes can track the referral campaign progress, based on which you can make your future strategies.
Ready to sell?
SaaS is built differently. There’s no one common sales strategy that works for all SaaS businesses. It’s all about experimenting with game plans for your business, and your product to get the right mix. So pick up the best strategies that suit your company. Track and review how they work. Make adjustments when needed, and never stop trying.